

The ISO 3864-1:2011 standard states that “there is a need to standardise a way of conveying safety information that depends as little as possible on the use of words to gain understanding.” Safety symbols are identifiable visual labels that indicate workplace, establishment, and public safety regulations. In addition, they alert people to potential hazards, dangers, or risks. Fire safety symbols provide instructions, cautions, and messages regarding fire safety. In situations that need a rapid reaction, they speed up understanding. Also, these symbols decrease accidents and raise awareness of risks in specific places or materials. Let’s dive deeper into fire safety symbols in this article.
Table of Contents
What is Fire Safety?
Fire safety is a set of rules and actions meant to make fires less destructive. Fire safety intends to stop uncontrolled fires from starting. Besides, it prevents a fire from worsening and causing more damage after it has begun.
Fire Safety Officers in the fire department check facilities for violations of the Fire Code. Also, they go to schools to teach kids about fire safety. Usually, the Chief Fire Safety Officer or Chief of Fire Safety trains new employees in the Fire Prevention Division. They may also do inspections or give talks.
Suppose part of a building is under construction while people are living there. You must install fire safety symbols and signs to make them understand the risks. Therefore, fire safety symbols play an essential role in fire safety.
Difference Between Signs and Symbols
For millennia, people have used signs and symbols to communicate beliefs, information, and talents for specific jobs. Also, you may use some signs and symbols interchangeably since their meanings are optional. However, there are some differences.
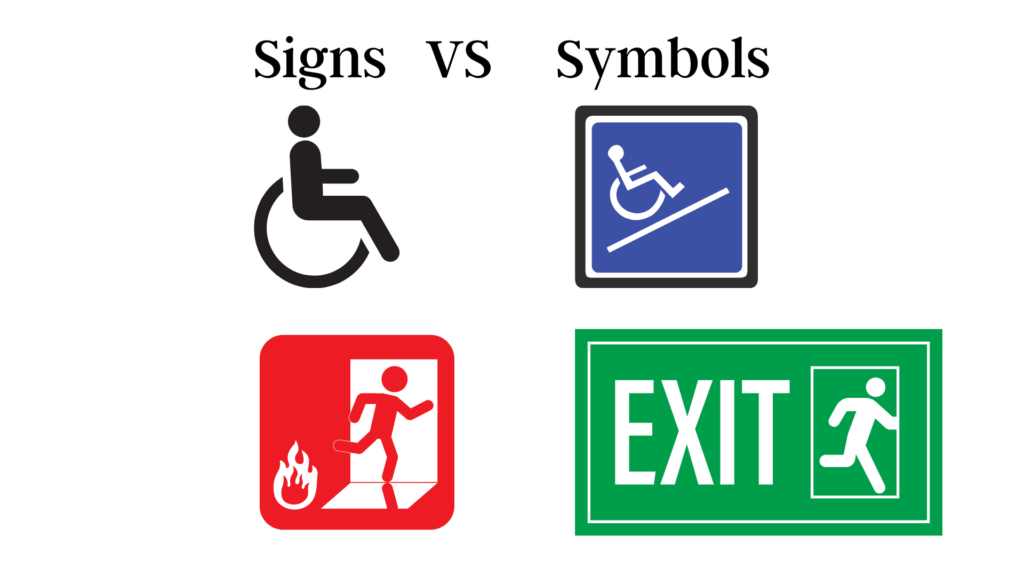
- Usage
We usually use symbols to encode or memorise important information. Such as
- the dove, which symbolises peace,
- the red rose, which symbolises love or romance,
- or black, which represents death.
However, signs are not cryptic and are typically literal. They convey ideas without words. For example, the wheelchair sign, which indicates wheelchair-accessible spaces, doesn’t need words. After seeing a wheelchair, you’ll understand the sign.
- Look
Symbols don’t appear like their meanings or everyday items. Thus they need prior knowledge or language to be understood. However, signs match their intentions. For instance, the signs on washroom doors indicating gender use imply precisely what they say.
- Colours
Signs don’t need colour to convey their meanings, but symbols do. For example, red flames signify more than yellow ones. Red is a more obvious threat than yellow. Whether black or blue, the wheelchair sign is a wheelchair.
What are the Fire Safety Signs?
Fire safety signs are visual cues for the workers or general people to understand the hazards. For example, “no smoking” may work as a safety sign in an area with combustible substances. Signs are simple yet efficient to visualise potential hazards. In addition, fire safety signs rely on something other than colours to express their meanings.
What are the Fire Safety Symbols?
Fire safety symbols are similar to fire safety signs. However, they can express different meanings through different colours. Also, they may be simple or complex according to their objectives. For example, a warning symbol with yellow colour is not as hazardous as a warning symbol with the colour red. So, there is a fundamental difference between signs and symbols. However, we’ll interchangeably use the words in this article.

Why are Fire Safety Symbols Important?
Sometimes engineering controls or safe systems of work cannot eliminate or mitigate hazards. In that case, employers must provide the appropriate fire safety symbols. In addition, fire safety symbols are vital to maintaining workplace safety. Also, individual safety is greatly enhanced when there are proper fire safety symbols in the building.
What are the Rules on Fire Safety Symbols?
Fire safety symbols follow The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations of 1996. Also, the Regulations apply to all locations and activities accessed by employees. In addition, these laws address numerous channels for disseminating safety and health messages. For example, it concentrates on
- illuminated signs,
- physical and audio signals, such as fire alarms,
- verbal communication,
- the labelling of pipes holding hazardous substances,
- fire escape signs,
- fire safety warning signs,
- and firefighting gear.
There is no need to issue fire safety symbols and signs if doing so will not make the area safer. However, it’s necessary to manage road traffic and the upkeep of fire safety symbols. Therefore, the regulations mandate the use of road traffic signs within workplaces.

Some Common Rules of Fire Safety Symbols
- Any door that may be mistaken for an emergency escape should be conspicuously labelled “no exit,” “no way out,” or “storeroom”.
- It would be best to put symbols at all direction changes in hallways, staircases, open areas, and above all doors or intersections along the exit path.
- Light fire safety symbols to guarantee visibility and legibility during power outages.
- Direction arrows on escape route symbols show the fastest route to safety. Therefore, you should always be able to see one.
- The arrowless emergency exit symbol should be above the final escape door. Instead, use a “running guy”, “exit”, or “fire exit”.
- Stick to either European Standard or British Standard signage.
- Fire safety guidelines should be in pictures with text to accommodate people with low vision, dyslexia, or who don’t speak English. The Disability Discrimination Act also requires braille and tactile fire safety signs.
- Fire safety training is mandatory for all personnel.
- Mark fire hose reels and extinguishers with signs.
Also, employers should educate workers on interpreting fire safety symbols. In addition, workers need to know what to do if they encounter anything unusual.
Fire Safety Symbols and Meanings
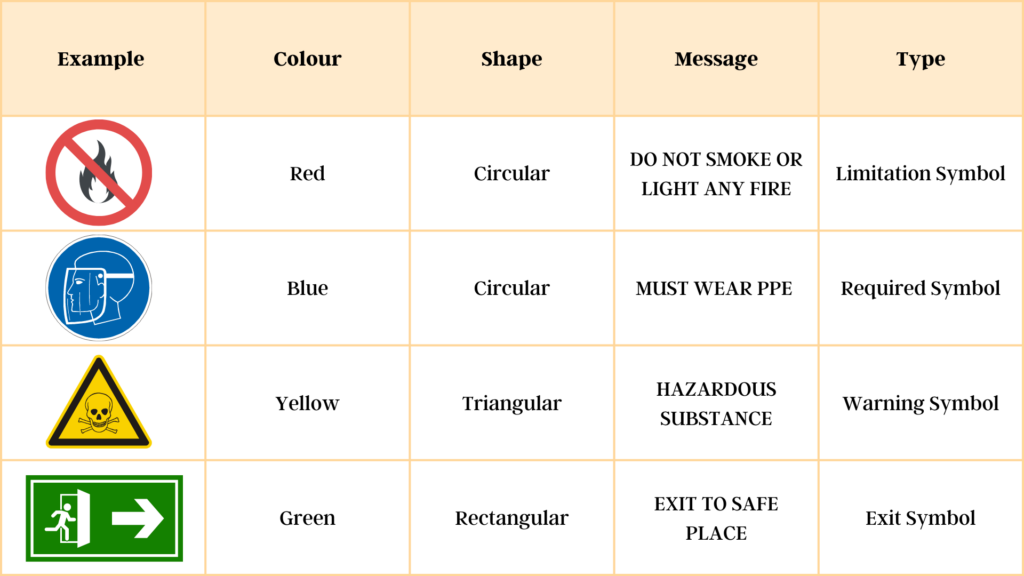
Fire safety symbols depend on the message they are meant to communicate. So, we can categorise safety symbols into different types. Also, we need to allocate specific structures and palettes of colours to each category. BS 5499 has explicit guidelines for allowed colour ratios and related dimensions.
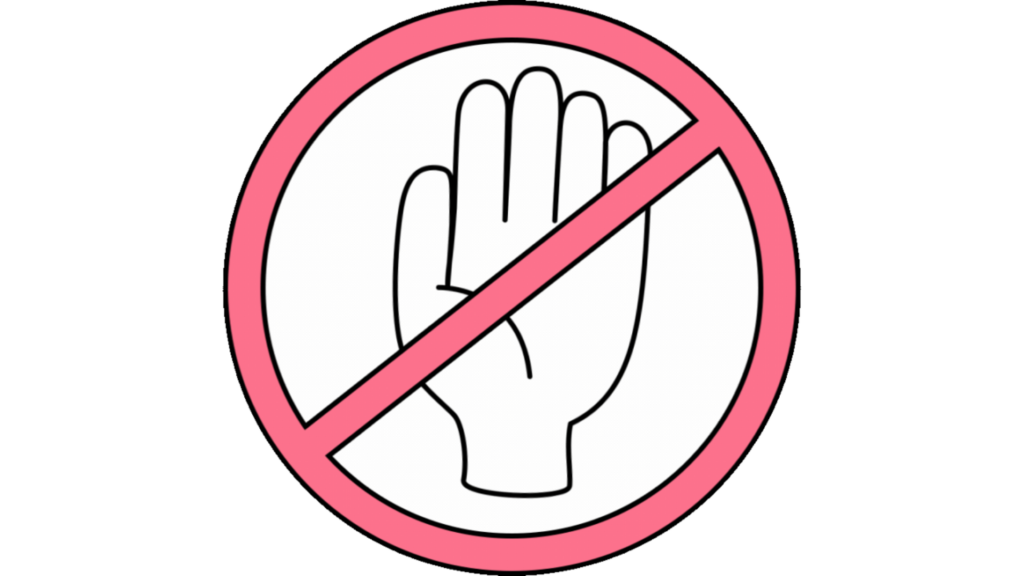
Limitation Symbols
These symbols represent the “do not” kind of order. For instance, a “do not use water” symbol expresses that a particular substance in that area reacts severely with water. In addition, a “no smoking” may suggest that smoking leads to a fire in that area. The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations of 1996 reinforce safety instructions. However, these guidelines are only impactful with proper staff training.

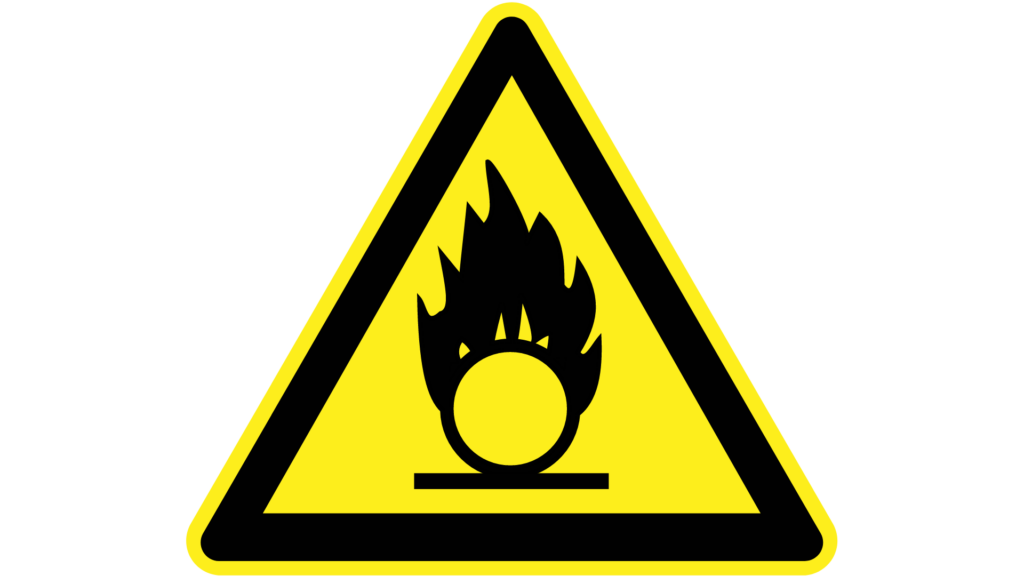
Alert Symbols
The purpose of these symbols is to alert passersby to potential hazards. For example, a suitable alert symbol should be close to the entrance of a facility that stores flammable liquids or a lab that uses radioactive materials. The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations of 1996 and, in some situations, the Dangerous Substances (Notification and Marking of Sites) Regulations of 1990 both call for the use of these symbols.

Required Symbols
These symbols identify tasks that you must complete adhering to legal obligations. For example, self-closing fire doors marked with the “FIRE DOOR KEEP SHUT” symbols at the entrance points comply with a fire risk assessment. Another example would be a construction site where you use the symbols of helmets.
They are required in the UK and part of most fire risk assessments. However, these symbols are not health and safety symbols under the Regulations. As a result, the well-known text-only, white-on-blue fire safety-mandated signs are left in place and do not need to be altered.

Safety Warning Symbols
These symbols mark emergency exits, first aid supplies, escape routes, and other essential locations. However, the Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations of 1996 do not mandate all UK fire safety symbols in this category. For instance, there is no symbol for “PUSH BAR TO OPEN”, and it is unnecessary to comply. Yet, such symbols must abide by the Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974 and, in some situations, the fire risk assessment.

Exit Symbols
Every doorway or exit offering access to a means of escape, other than exits in regular use, must contain an exit symbol to comply with the Building Regulations of 1991 and the Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals Regulations) of 1996.

In the meantime, whether you need to mark regular exits with symbols must then be addressed. If the hazard is not considerable, refrain from using symbols.
- Lighting Up Symbols
Exit signs must always be visible and readable. Regular lighting may fail in a building. In that case, lit the exit symbols with the emergency lighting source. Any of the following options are regarded as suitable:
- exterior lights that adequately illuminate the sign,
- internal lamps,
- internally lighted signs,
- and self-luminous signs that don’t need an external power source.

Photosynthetic Symbols
These symbols contain photoluminescent materials in their viewable parts. In addition, photoluminescent materials can absorb and store energy from natural or artificial lights. Now, numerous businesses create photoluminescent symbols with pictograms that adhere to the regulations. Albeit, the colours might not quite match the requirements.
These indications’ characteristics make them helpful as a complement to typical symbols in specific circumstances. For instance, they function effectively as signals when the usual light source fails and emergency escape lighting is in use. HSE regulations permit the use of photoluminescent materials as an addition to emergency lighting. However, this lighting cannot replace emergency lighting.
Fire Fighting Equipment Symbols
These symbols indicate the locations of fire fighting supplies and fire alarm activation sites. Fire apparatus, however, should always be placed where you can see it easily. The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations of 1996 provide that the colour red must identify firefighting gear. The equipment will meet the criterion if it is red. Where the backdrop is not red, emphasising the location of firefighting equipment by painting the background red may be sufficient to meet the requirements.

What are the Different Colours of Fire Safety Symbols?
Fire Safety Symbols require different colours to express different meanings. For example, a red colour doesn’t instruct the same as a blue colour. The most common three symbol colours are red, blue, yellow, and green.
What Does Red Colours Express?
The colour red is the universal symbol of danger. Therefore, you always see red traffic lights and stop signs on the road. Red fire safety symbols indicate exits and other vital information in the event of a fire. In addition, they serve as a source of information in high-risk areas for wildfires.
You may find the colour red frequently on prohibition signs. It explicitly states that a particular action is forbidden. Also, many no-entry symbols have a black emblem on a white backdrop within a red circle to indicate what’s banned. Employers or authorities often use red symbols as warnings against smoking.
In psychology, red is associated with danger and serves as a warning to desist. Therefore, it’d be best to display essential safety indicators in bright red to grab people’s attention.
What Does Blue Colours Express?
When a safety symbol is blue, it means people always adhere to it. Mandatory instructional symbols must be blue. In addition, they feature a white image set against a blue backdrop. Blue symbols are typically used in professional settings to inform users of their next steps. Also, they remind employees to take standard precautions, such as donning safety shoes, hard hats, and fluorescent vests. The majority of the time, these are located at building sites. Some symbols should be up as a means of communication and offer directions, such as where the site office is.
The colour blue is soothing to the eye without being seen as dangerous. Moreover, many people identify the colour blue with education. Therefore, it has been the standard for required symbols since establishing the regulation in 1996.
What Does Yellow Colours Express?
Among the fire safety symbols, the yellow symbol indicates the presence of a specific hazard. The hazard may come with the use of a substance in the workplace. As a result, yellow symbols are often referred to as “warning symbols”. They must be yellow or amber with a black emblem at all times. The border and lettering on them are often black.
Yellow warning symbols often warn of excessive voltage, death risks, or trip hazards. Also, yellow draws attention to important information like warnings and guidelines. Based on studies of human perception, the colour yellow is the one that catches people’s eyes first. Therefore, using yellow for warning signs and caution tape increases their visibility.
What Does Green Colours Express?
Green is a well-received colour since its association with nature and safety. Green traffic lights indicate that it is safe to cross the street.
Green symbols point the way to a secure location or path free of danger. These symbols show the locations of emergency exits. In addition, they indicate areas where you can administer the first assistance. Green fire safety symbols contain a white emblem and text against a green backdrop when used as directional or emphasis symbols.
What are the Different Classes of Fire?
All fires require an ignition source, fuel, and oxygen.
Fuel sources include
- wood
- paper
- loose packing materials
- discarded garbage
- plastic
- rubber or foam
- and furniture
On the other hand, ignition sources include
- heaters
- lighting
- exposed flames
- electrical equipment
- and smoke materials
Oxygen sources include
- the air we breathe
We can divide flames into five broad categories based on their origin or the burn materials. In addition, it’s better to identify the most significant fire risks at your site. Then you’ll be able to prepare for a fire emergency effectively. All in all, learning about these five types of flames is vital to a place’s fuels and fire hazards.
Classification of Five Types of Fires
- Class A : Solid objects including wood, paper, cloth, and some polymers.
- Class B : Oils, fats, and other lubricants that can be turned into liquids or gases.
- Class C : Power outages caused by home electronics, appliances, or wiring.
- Class D : Sodium, titanium, zirconium, and magnesium.
- Class K : Specifically related kitchen grease or oil fires.
- Class A
The majority of fires fall under Class A. They take place when ordinary combustibles catch fire. For example, the objects can be wood, paper, cloth, rubbish, or light plastics. There is a prevalence of these types of fires across many different sectors. Therefore, it is wise to take precautions against Class A fires. In the presence of a large amount of fuel, these flames can spread rapidly. In this case, use water or monoammonium phosphate to extinguish a Class A fire.

- Class B
Flammable liquids and gases are the primary cause of Class B fires. For example, petroleum-based goods like gasoline, paint, or kerosene can cause a Class B fire. In addition, propane and butane are two more highly flammable gases that frequently start Class B fires. In this case, smothering the flames or cutting off their oxygen supply with foam or carbon dioxide suppression is the most effective fire extinguishment.

- Class C
Class C fires are most prevalent in manufacturing and processing plants. However, they can happen anywhere. Faults in electrical equipment can cause Class C fires. For example, data centres are prone to electrical fires. Also, Class C fires are not uncommon on construction sites due to the prevalence of electrical power equipment. In addition, there are cooking appliances that can generate sparks that ignite flammable items and quickly spread. Besides, more risks are associated with older buildings with faulty wiring or space heaters.
Water is ineffective against electrical fires.
Water conducts electricity. So, it’s best to avoid it.

- Class D
Class D fires are less prevalent than those in the other categories. Nonetheless, stay careful due to their high difficulty rating. In addition, there are different materials involved in metallic fires. For example, titanium, aluminium, magnesium, and potassium are combustible. Also, it’s unsafe to use water on a Class D fire. The best way to put out a fire and prevent further injury or loss of property is with dry powder agents.

- Class K
Class K fires are unique to the restaurant and food service industries. The ignition of flammable liquids causes most kitchen fires. Class K fires spread rapidly, and they are challenging to control. Therefore, it makes them very deadly. In this case, smothering the flames or using a wet agent fire extinguisher are better options than water.

Summary
Fire safety symbols play a vital role in minimising fire hazards. However, every worker must adequately understand the fire safety symbols. In addition, businesses have to give their workers fire safety training under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, the Fire Safety (Scotland) Regulations 2006, and the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005. Therefore, it’d be best to train yourself or your workers in fire safety. Our Fire Safety Training Course will teach you some of the most critical fire safety concepts. In addition, this introductory Fire Safety Course will educate you on what procedures need to be in place and how to react professionally if a fire emergency occurs.
- Available Courses
- Animal care10
- Design28
- Training9
- Accounting & Finance Primary50
- Teaching & Academics Primary37
- Teaching23
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed181
- Law10
- IT & Software230
- Job Ready Programme52
- Charity & Non-Profit Courses28
- HR & Leadership4
- Administration & Office Skills4
- Mandatory Training36
- Regulated Courses4
- AI & Data Literacy26
- Health and Social Care290
- Personal Development1632
- Food Hygiene119
- Safeguarding80
- Employability288
- First Aid73
- Business Skills296
- Management425
- Child Psychology40
- Health and Safety533
- Hospitality28
- Electronics30
- Construction63
- Career Bundles201
- Marketing39
- Healthcare172

 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development




