PAT Testing (Portable Appliance Testing) checks electrical appliances through different electronic tests. PAT testing is vital for ensuring safety. So, go through this blog to understand PAT testing and how to become a pat tester.
In this blog, you will learn:
Table of Contents
What is PAT Testing?
Before learning how to become a pat tester, you should know about the PAT test. A PAT test is a routine assessment of electrical instruments to check they are safe to use. Its aim is to stop electrical accidents in the workplace.
Portable Appliance Testing is the easy, quick, and accurate testing of electrical equipment. In addition, a full PAT test should include a visual examination and a more in-depth check using specialist PAT testing tools.
Why is PAT Testing Carried Out?
The primary reason to execute a PAT test is to ensure safety. So, PAT tests are essential to upholding the safety standards of electrical appliances in your properties.
Remember, it’s good to be safe rather than sorry.
With an ever-increasing number of fake electrical products in the market today, ensuring your electrical products are legitimate and secure is essential.
So, you should perform a PAT test after any new purchase of electrical products and then, at regular intervals, check for issues and maintain safety standards.
Who are PAT Testers?
PAT testers are professionals who are experts in doing PAT tests. An expert with the required knowledge should conduct PAT tests and any electrical work to avoid risk to themselves and others.
What does a PAT Tester do?
PAT testers detect potential safety issues with electrical instruments. Besides, certified PAT testers can help you check electrical devices while ensuring safety.
For example, if you try to do a pat test yourself without proper knowledge, you might get an electric shock. So, be careful enough to avoid such incidents. So, to stop workplace risks, managers and responsible employees must conduct maintenance check-ups.
Who can Carry Out PAT Testing?
Anyone can PAT test their equipment; if they are a competent person with the relevant training, knowledge, equipment and time. Maybe you are thinking about how to become a pat tester and do it yourself.
One can take a PAT training course to be capable enough to perform PAT testing. Also, an instructor will take a knowledge test to ensure you have gained enough knowledge on pat testing.
Pat testers use electrical tools and have responsibility for electrical supervision. So, they may need more detailed technical skills.
Besides, owners and managers are also liable for ensuring PAT testing in their companies.
What are the PAT Testing Requirements?
The law requires an employer to ensure that their electrical equipment is in good condition and safe to prevent danger. However, the law does not say how you will do it or how often. Thus, employers should take a risk-based approach, considering the type of equipment and its use.
Before thinking about how to become a PAT tester, make sure you have the required skills and abilities. Additionally, the law states that the individual must be competent for the PAT test. The qualities of a qualified person are –
- Have sufficient knowledge of electricity.
- Have enough experience in electrical work.
- Have adequate knowledge of the system to be worked on and practical experience with that type of system.
- Understand the dangers that can occur during the work and the protection that must be taken.
- Have the ability to determine whether it is safe for work to continue.
PAT Test Legislation
PAT testing regulations will ensure that the portable appliances in your firm are safe and help you avoid risks. Besides, PAT testing legislation ensures that all companies coordinate with some legislation, such as –
Moreover, the current law demands that all employers carry out pat tests. Authorities can do this by testing the instruments to avoid potential risks.
PAT Testing Legal Requirements
There is currently no strict legal condition for PAT testing. However, the Government has imposed rules that relate to the maintenance of electrical instruments. Besides, PAT testing is the most helpful way to ensure these regulations are met.
Even though PAT testing is not a legal need but can count towards the care of electrical tools. Also, there is no legal rule to involve PAT testing stickers on tested appliances.
How Often Should You PAT Test?
There are no strict guidelines surrounding the frequency at which you should have your electrical appliances PAT tested. However, in the sections below, we have outlined some best practices for PAT testing in various industries.
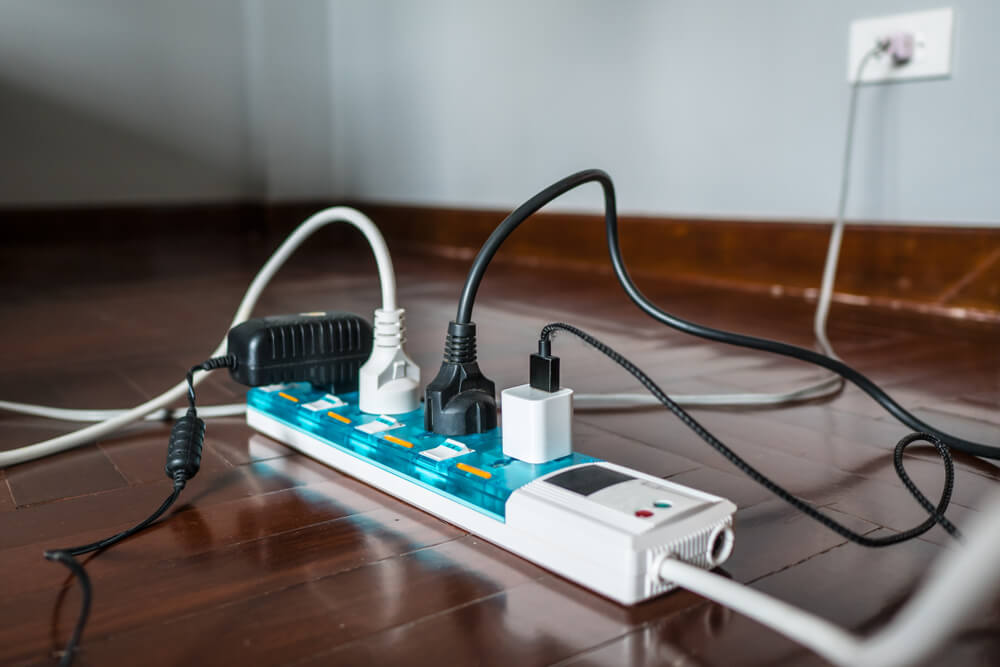

The frequency of testing depends on the type of equipment and its condition. For example, a pat tester should test a power device used on a construction site more than a light in a hotel bedroom. For suggestions on recommended frequencies of inspection and testing, check the following:
Offices, shops, hotels and alike
- Class 1 (general IT equipment) should be examined every four years.
- Portable tools, such as attachment leads, should be tested every two years.
- Handheld and more often used and transported supplies should be tested every 12 months due to the increased risk of damage.
Schools
- Test All class 1 and IT equipment every year.
- Test Class 2 equipment every two years.
Construction
- All 110V equipment regularly used on a construction site should be tested as often as every three months!
Industrial
- Industrial sites, including retail kitchens, should have their portable and handheld equipment tested as often as every six months.
- For other stationery, portable or IT equipment, it is advised to test every 12 months.
Do You Need a Qualification for PAT Test?
You don’t need any specific qualifications for the PAT test. Yet, the regulations demand that a competent person does the testing. A skilled person is – “Someone with enough technical knowledge to avoid potential risks and injuries.”
Additionally, the legislation considers that any competent person can perform it using a PAT instrument. So, the visual inspection of each appliance and the actual PAT test should be conducted only by someone considered qualified.
According to PAT testing legislation, a competent person is experienced and capable of testing appliances. Thus, those with knowledge of electricity in general and anyone with a background in electrical work can be deemed competent.
Besides, you can get a good understanding of how to become a pat tester by taking proper training.
How to Become a PAT Tester?
The law suggests that anyone who wants to be a Portable Appliance Tester (PAT Tester) should be deemed competent at PAT Testing. Therefore, to become a PAT tester, you start a PAT Training course and gain certification.
Additionally, If you are curious about doing a PAT Test Course to learn from a specialist on a one-to-one level, look at our PAT training courses.
Moreover, to receive PAT testing qualifications, you must complete a PAT tester course to learn how to become a pat tester. It is available from many providers, some of which require previous electrical experience to qualify as an official PAT tester.
Penalties if You Don’t Meet the Legal Obligations
Depending on the circumstances, the penalty for not meeting legal obligations on electrical appliance safety can be up to 2 years of confinement and a financial fine.
PAT testing directs the safety of any portable instruments plugged into your electrical system. While there are no penalties, especially for PAT testing, failure to keep equipment safe could cause a violation of corresponding laws, including the Electricity at Work regulations (1989) and the Health and Safety at Work Act (1974).
Besides, as is also the issue for EICR non-compliance, this might result in substantial financial penalties and even imprisonment. If someone is harmed on your property, the courts will look for PAT and EICR testing to inspect whether you were at fault.
However, regular testing is easy to stop accidents and protect yourself and tenants or employees. That’s undoubtedly backed up by a series of penalties in 2018, ranging from £1,560 to £45,000. A total of 15 businesses – including e-commerce platforms eBay and Gumtree – were non-compliant, facing a combined penalty of £157,770. So, while online companies might be able to clear their fine of £12,150 each, it might not be easy for a typical UK business.
You can avoid all of these penalties by understanding the laws and getting training. Also, you need to learn how to become a PAT tester.
Other Consequences
Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) demands companies report their energy usage and carbon emissions. While forfeitures are yet to be published, it’s thought they could be as much as £40,000.
Like EICR and PAT testing, fire warnings aren’t subject to specific fines for non-compliance. Additionally, forgetting to maintain them correctly will breach other rules, such as the Fire Safety Order, which will leave you liable for any damage or harm caused by fire on your premises.
Moreover, this can result in unlimited penalties and up to two years in prison, with penalties of £5,000 for minor crimes. In February 2021, for instance, a pub/ bar in Bristol was fined a whopping £120,000 after managers were found to be relaxed about fire safety laws – even though nobody was harmed.
Who is Responsible for Ensuring Equipment Safety?
Business owners and employers are responsible for equipment, workplace health and safety. Also, they need to keep their employees and customers safe from harm.
Apart from this, no person is solely responsible for workplace health and safety or equipment safety. It’s merely too big a task for a single person. So, the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) expects business owners and staff to share the responsibility.
But that’s not to say obligations are shared equally. Staff in different roles will have other equipment safety duties to uphold. For example, employers hold more responsibility than their staff. They are responsible for the safety and well-being of their workers.
Learn how to become a PAT tester to understand the rules and responsibilities well.
What is the Meaning of ‘Electrical Classes’ in PAT Testing?
We can categorise electrical appliances as Class 1, 2 or 3, with Class 1 being the most dangerous while Class 3 is the least risky.
The class of an instrument helps decide whether it needs to be PAT tested and to what degree. For example, class 1 appliances need a full PAT test, Class 2 devices require a PAT insulation test, and Class 3 appliances don’t require PAT testing.
Class 1 Appliances
This type of electrical equipment has only essential insulation and relies on the earth for safety.
Class 2 Appliances
This type of electrical equipment has additional insulation and doesn’t rely on an earth for protection, making it securer.
Class 3 Appliances
Class 3 appliances are low-voltage objects and the most protected electrical appliances. However, their charging leads may require to be PAT tested.
Top Features of Different PAT Testers
PAT testing tools have different levels of functionality. Yet, basic PASS/FAIL kits are easy to use and affordable. As a result, they are the best option for all ranges of businesses.
The PAT100 series of hand-held transportable instrument testers enable uncomplicated, fast safety testing in all environments, including shops, business units, and offices. In addition, It is ideal for training organisations, rugged and dependable, easy to learn, yet fully functional. With armoured rubber cases and hardened, scratch-proof glass, the PAT100s are quite complex instruments that can cope with the treatment they will undergo on-site or in the van.
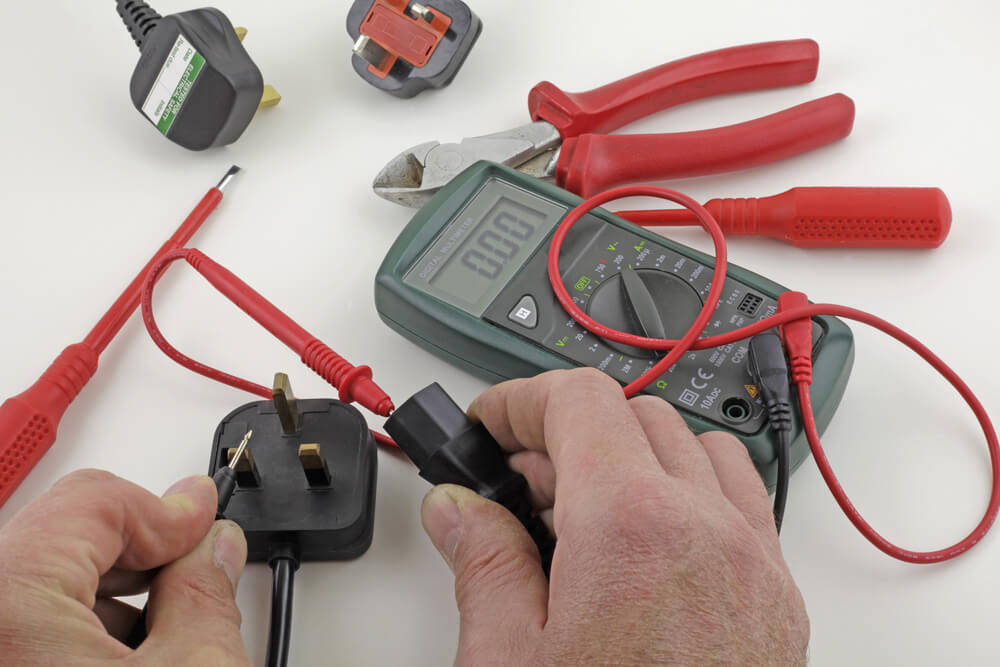

There are Three Testers in the Range
First: PAT120 offers Class I, Class II, power and attachment lead testing with fixed pass limitations. It has two insulation test voltages. Use it to test IT and surge-protected tools.
Second: The PAT150 full functionality PAT tester offers portable RCD (PRCDs) testing at ten mA and 30 mA.
Third: PAT150R is an upgraded and rechargeable version of the PAT150.
Moreover, some PAT testers show the entire set of results. These PAT testing models are user-friendly and feature basic interfaces, enabling test results to be taken and recorded. Apart from these, PAT kits are inappropriate for testing the complete range of electrical gear. Besides, most models lack functionality for the configuration of test parameters.
Again, advanced PAT testing kits are fit for users with a high level of technical proficiency and expertise. Moreover, these advanced techniques are particularly appropriate to facilities management, as they record the location and test status of gear and machines.
Some procedures can also transfer the test results to computers for digital interpretation. In addition, PAT software can control and maintain test records.
The PAT400 Series
They are appropriate for performing portable appliance testing in locations such as hotels, theatres, banks, cafés, cafés, sports, public houses, schools, colleges, nurseries, shops, offices, cinemas, factories and hair salons etc. High volume testing requires where correct records may be difficult to possess, or aided by, onboard memory and download to management software.
Besides, the PAT400 is appropriate for tool-hire shops where supplies are routinely tested before hire or service. Workshops, where deep disassembly is routine, will conduct a flash test in addition to standard PAT tests.
PAT410 is excellent for those ranging to bond test solely at 200 mA. The lightest and smallest of the PAT400 series weighs only 2.7 kg.
PAT420 offers bond testing at all three ranges, 200 mA, 10 A and 25 A and 230 V and 110 V. This tester is the choice of full-time commercial or industrial PAT testers.
PAT450 includes 110 V and 230 V operations. In addition, this tester offers 3.0 kV and 1.5 kV flash testing making it the ideal device for hire and repair workshops.
The PAT 400 series introduces a unique level of convenience and speed to PAT testing using onboard test outcomes.
How to Carry Out a PAT Test?
A PAT tester is the only piece of instrument you need to conduct a PAT test. There are different kinds of models in the market and if you’re a business requiring these tests, it’s worth investing in one.
First, plug the electrical device into the PAT tester, and press the right button depending on the appliance class. So, if it’s a class one machine, you would press the class one button. It will then give three readings: one for insulation opposition, one for lead polarity and one for earth continuity. It will then provide a fail or pass grade.
Then it is necessary for the tester to log the results in a supplies test record log. This should include all visual information about the machine and the readings given by the PAT tester.
Besides, examine the cable, cuts, abrasions, and cracks. Make sure that plugs, sockets, flex outlets, and isolators are always available to enable disconnection of the supply. (either for functional, maintenance or emergency purposes.)
Finally, as an extra layer of security, you should add a PAT test label to the equipment. Labels are a good contingency if the equipment test log is lost or destroyed. Don’t stress yourself thinking about how to become a pat tester and carry out a pat test. Instead, take proper preparation and training first.
PAT Test Preparation
PAT testers must understand the mechanical failure of the instrument. So, to carry out pat testing, the first step is preparation.
In the beginning, you should follow these two steps.
Firstly, conduct a visual inspection to find potential faults in the equipment, cable, and plug.
Secondly, ask about flaws in the user experience. It defines factors that will rely on the electrical equipment, the equipment itself and its risk dimensions. If possible, conduct a resistance to insulation test to review the current leakage.
Earthing Continuity Testing
It is a method where the equipment’s shielding is immune to the earth circuit that does not overreach 1 Ω. In addition, the tester has options to use different tests depending on the circumstance.
Safety Switches Test
If there is any electrical defect, the safety switch can stop the electricity supply. It minimises the risk of electricity-related fires, injury and death and electric shock. To test, firstly, push the test button on the safety switch. This should automatically trip the button to the off position, and you will hear a ‘clunk’ sound. Secondly, you should review inside your home to see which lights or devices are off.
The circuits turned off by the safety switch test mean they are protected by it. After completion of the assessment, the tester must prepare a report on the equipment. Also, give some guidance on further action.
Summary
Portable Appliance Testing is the inspection of electrical equipment. It ensures they are safe to use. Also, PAT testing provides safety help in preventing workplace electrical casualties. PAT testing is not a legal condition. However, the UK legislation states that all companies must keep all electrical devices safe.
Also, the legislation suggests ensuring the health and safety of the employees. And now you also know how to become a PAT tester. So, if you want to learn PAT testing, proper training and planning on becoming a PAT tester is a brilliant step.
FAQ(s) on PAT Testing
A PAT (Portable Appliance Testing) tester is a professional responsible for ensuring that electrical appliances are safe for use in various settings, such as workplaces, schools, and public buildings. The process involves examining the equipment for any defects and conducting safety tests.
- PAT stands for Portable Appliance Testing.
- The tester is responsible for checking the safety of electrical appliances.
- The role involves both visual inspections and technical testing.
In the UK, while appliances are not legally required to undergo PAT testing, it is considered best practice. Many businesses and institutions require it to comply with health and safety regulations, ensuring that they meet the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 requirements. Being certified ensures that you are competent in performing these tests accurately and safely.
- PAT testing helps businesses comply with the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989.
- It is considered a best practice, though not a legal obligation.
- Certification demonstrates competence and assures clients of your skills.
The frequency of PAT testing depends on the type of equipment and its usage. For instance, equipment used more frequently may require more regular checks. It's best practice to have an assessment of your equipment to determine the appropriate testing intervals.
- Regularly used equipment may need more frequent checks.
- An assessment can help determine the ideal testing intervals.
While PAT testing itself isn't a direct legal requirement, the UK's Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 mandates that electrical equipment must be maintained to prevent danger. PAT testing is a widely accepted method to ensure this safety standard is met.
- PAT testing isn't directly mandated by law but is a recommended practice.
- It ensures businesses and institutions maintain safe electrical equipment.
All electrical appliances that have a plug and are intended for connection to the mains electricity supply should be considered for PAT testing. This includes computers, printers, refrigerators, kettles, and even extension leads.
- Appliances connected to the mains electricity supply should be considered.
- This encompasses a wide range of items, from computers to kettles.
- Even extension leads are included in the list.
A visual inspection involves physically checking the appliance for signs of damage or wear that might make it unsafe. It's the preliminary step before a PAT test. A PAT test, on the other hand, involves using specialized equipment to conduct electrical tests, ensuring the appliance's safety from an electrical perspective.
- Visual inspection checks for physical damage or wear.
- It's the first step before conducting a PAT test.
- A PAT test uses specialized equipment for electrical safety checks
The Health & Safety Executive provides no set law or regulation on PAT testing frequency or how long PAT tests last.
Employers, landlords and self-employed require PAT testing to ensure the safety of portable appliances. Therefore, you should do a PAT test regularly to ensure preventative supervision.
There is no announced end date for the PAT test certificate. Thus, you should re-test Class 1 electrical equipment every 48 months and Class 2 electrical instruments every 24 months.
Yes, you can carry out PAT tests if you think you are a 'competent' person with sound knowledge about PAT. If you choose to do your PAT testing, first, you should take a professional PAT - Portable Appliance Testing Training Course.
Read More Articles on Electrician Career and Safety
- Available Courses
- Career Bundles73
- Animal care5
- Law8
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed111
- Teaching13
- Teaching & Academics Primary27
- Accounting & Finance Primary30
- Training3
- Design9
- IT & Software44
- Healthcare126
- Marketing31
- Health and Safety402
- Construction48
- Electronics25
- Hospitality22
- Health and Social Care219
- Child Psychology37
- Management377
- Business Skills268
- First Aid70
- Employability264
- Safeguarding75
- Food Hygiene103
- Personal Development1277
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development