

Thanks to HACCP, we can rest assured and have restaurant food freely. So do you have any idea about what is HACCP or, what are the 7 principles of HACCP?
So many of us enjoy our best moments over delicious food in a restaurant somewhere in the city. Dating, enjoying a favourite burger with friends and ordering pizzas with family or just grabbing lunch on a busy workday, and it goes on.
Moreover, our daily raw food rations come from some food operators like grocery stores, butchers. But how many times do we wonder if the food is hygienic or made in a clean place? Except for the ones with germophobia, we hardly give a thought to it. But the 7 principles of HACCP does.
So let us grab a look at the details of HACCP and why a restaurant needs to maintain HACCP. If you own a restaurant, you can also learn why your restaurant hygiene is compulsory for your business. Finally, what are the 7 principles of HACCP that all restaurants should take care of? Not to worry, this blog will answer all these questions and help you enjoy your restaurant meals.
What is HACCP?

The full form of HACCP is Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It is an international management system to identify food hazards and ensure food safety. HACCP is a preventive approach to food safety. Therefore, it considers all the food safety issues that occur due to biological, chemical, physical hazards, and radiological hazards during food production. It is done by following the 7 principles of HACCP.
As a result, the 7 principles of HACCP identify those food production hygiene issues and take actions to prevent them. In this way, instead of inspecting finished products for the effects of these hazards, HACCP attempts to avoid hazards throughout the production process. Therefore, the HACCP system is suitable for all food chain steps, including packaging, supplying, and other food production and preparation processes.
The formation of HACCP was in 1960. When NASA asked Pillsbury to design and manufacture the first foods for space flights, it was the triggering point of HACCP. HACCP has since gained international recognition as a rational tool for adapting traditional inspection methods into a modern, science-based food safety system. Many of the world’s best manufacturers and vendors now use the framework as the foundation for their food safety management systems and GFSI inspection requirements.
If you run a food business in the UK, you must make a food plan depending on HACCP principles. You and your team should make sure that the food produced by the business is safe to eat under Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 Article 14.2. As a result, it will indicate that the food is not harmful to human health nor unsafe for consumption. To do so, Article 5 of Regulation (EC) 852/2004 allows all the food suppliers to put in place, execute, and maintain HACCP principles at all times.
Why is HACCP Important?
Due to poor hygiene and the unclean food preparation process, foodborne illness and allergic issues can make people suffer. Bacteria and other microorganisms can easily infect food and multiply rapidly. If this diseased germ gets into the human body, it can create a life-threatening illness. The main work of the HACCP plan is to make our foods healthy and contamination-free as much as possible.
In an article in Food Safety News:
“Researchers have estimated there are 180 deaths per year in the United Kingdom caused by foodborne diseases from 11 pathogens. The Food Standards Agency (FSA) estimates that about 2.4 million cases of foodborne illness occur every year in the UK.”
Moreover, HACCP also helps to prevent any allergic reactions. Particularly in cases of anaphylactic shock, which people can avoid if they know exactly what they’re eating. Food producers make sure that they are labelling their food or mention all the ingredients that go into the food preparation. So HACCP also looks after if the food is carefully labelled and packaged.
HACCP is vital in the food industry to monitor potential food hazards and tries to minimize the risk. The industry can better ensure customers that they are safe to eat their food. That is because it incorporates good science and technology to regulating major food risks, such as microbiological, chemical and physical contamination. HACCP increases Public health safety by reducing foodborne hazards.
Therefore, restaurants and other food-producing businesses can build more reputation among customers by enforcing the HACCP plan.
What are the 7 principles of HACCP?

In order to ensure the food that we consume is made with care and is pathogen-free, the food industry should abide by the 7 principles of HACCP. For those working in the food industry or who want to open their own food business, you need to have a clear knowledge of the HACCP principles. As your processes change, your company grows, and you discover better ways to produce your product, you must also reassess your HACCP plan frequently.
For carrying out the HACCP plan, you need to be an expert in it or include a HACCP management system in your business. Below you can find all the 7 principles of HACCP and their details.
Principle 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis

The very first condition of the 7 principles of HACCP plan is to identify and do a risk analysis. You or your HACCP team must recognize where there is a chance of hazard and list them out.
A hazard is the possible biological, chemical or physical agent that is likely to cause illness or injury if there is no proper control system. For example, cross-contamination of harmful bacteria from raw food to cooked food, mix of toxic detergent with food from utensils, or finding harmful metal or glass pieces in the food. HACCP plan should concentrate on preventing, eliminating, and controlling these hazards in all the steps of food production.
Observe each step of food production. Everything should go under hazard analysis from purchasing raw ingredients, delivery, storage, preparation, cooking, and chilling. List down all the potential hazards in association with each step that is under the direct control of the food production. If there were health-related issues previously regarding the product, take them into account.
There are three objectives of carrying out hazard analysis:
- First, hazards should be identified along with associated control measures required for them.
- The analysis can detect the need for changes to a process or product in order to ensure or enhance product safety.
- The analysis gives a basis for determining the Critical control point in Principle 2.
You must do Hazard analysis carefully and thoroughly. If the analysis is not done correctly, and you cannot find the hazard factors. As a result, the rest of the plan will not work correctly.
Principle 2: Identify the Critical Control Points

The second principle is identifying and forming necessary prevention measures to eliminate or reduce hazards to an acceptable level.
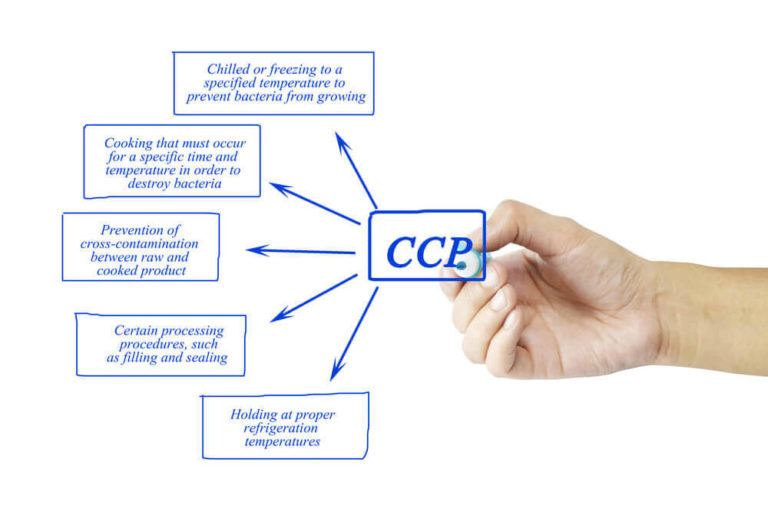
A critical control point (CCP) is the process to find and take necessary prevention measures. A CCP may manage more than one food safety hazard. In some cases, multiple CCP is necessary to control a single hazard. The total CCP required is determined by the processing steps and the level of food safety control necessary.
Controlling food safety hazards requires the complete and accurate identification of CCP. The HACCP team needs the information gathered during the hazard analysis to determine CCP. The use of a CCP decision tree is one technique for making it easier to identify each CCP.
Some examples of the CCP are detecting suitable temperature, pH level, chemical residue testing in ingredients, product formulation monitoring, and metal contamination testing. CCP, therefore, should be carefully developed and documented to prevent hazards.
Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits

After identifying the CCP, you need to establish the critical limits for it. Critical limits are the range of maximum and minimum biological, chemical, or physical factors at a CCP that must be controlled. At a CCP, a critical limit is helpful to differentiate between safe and unsafe operating conditions. It should be established in a way that eliminates or reduces potential hazards.
Food is safe to eat if it is cooked or processed under a specific condition. Setting critical points helps to process the food under that condition. For example, cooking meat products at a standard temperature will kill germs or maintain certain products’ pH to preserve them properly.
Critical limits are scientifically, and they are factors such as:
- Temperature
- Time
- Physical state
- Humidity
- Moisture level
- Water activity
- Acidity or Alkalinity(pH)
- Titratable acidity
- Salt concentration
- Available chlorine
- Viscosity
- Preservatives
- Sensory information such as aroma and appearance.
Principle 4: Monitor CCP
The fourth principle of the 7 principles of HACCP is monitoring CCP. When you are complete with establishing critical limits for a CCP, it is time to monitor its procedure.
Monitoring requires planning and sequential observation done to see all the CCP is under control. It checks the established critical limits for each CCP and measures if it is working correctly. Monitoring processes must describe how to do the measurement, who is responsible for the measurement, and how often to do the measurement during the production process.
Therefore, monitoring is a systematic process that should be recorded to be used in the verification process. There are three main reasons to monitor your critical point:
Firstly, monitoring is an important part of food safety management and helps to track hazard prevention operations. If you find any issues during monitoring, you must take necessary action for it.
Second, monitoring helps to assess whether there is a lack of control. It is because a problem occurs at a CCP because a critical limit is exceeding or not met. You and your team have to take proper corrective measures when a deviation occurs.
Thirdly, it provides detailed documents that can be used for verification later on.
Principle 5: Establish Corrective Action

Even with critical limits and food safety management in process, problems can occur at any time, which can cause a health hazard. When any kind of problem occurs, or there is a deviation in critical limits, you have to take corrective action for it. Whenever there is deviation, there should be corrective action for it to prevent further hazards.
You and your HACCP team must identify what kind of measures should is essential to avoid a potential hazard or hazardous food or ingredient getting into food chains. To take corrective action, you have to solve the problem immediately and stop it from occurring again.
As a result, corrective action must have the following elements:
- Determine and correct the cause of non-compliance;
- Determine the disposition of the non-compliant product
- Record the corrective actions that are already done.
You have to form corrective action beforehand for different CCP and must be inside the HACCP plan. At the least, when a specific deviation occurs, there should be instruction for corrective action in the HACCP plan. It will save time, and businesses will know what to do about it.
Also, you must assign corrective action control to people who clearly understand the process, product, and HACCP strategy. You can consult experts if you need to review the information and decide how to dispose of non-compliant products.
Principle 6: Verification

Verify all the activities that are in place to prevent hazards are working properly and doing their work. You have to determine if your HACCP system is working according to the plan. An FDA article states that:
“The NAS (1985) (2) pointed out that the major infusion of science in a HACCP system centres on proper identification of the hazards, critical control points, critical limits, and instituting proper verification procedures.”
Firstly, verification necessary to validate if the HACCP system is working according to the plan. Verify if the outcomes are as expected and prevent hazards efficiently. Secondly, verify that the plan is scientific and technically sound. The plan must identify all hazards and effectively control these hazards if the HACCP plan implementation is correctly taking place. In order to validate the HACCP plan:
- Take help of expert advice and scientific studies.
- Obtain information on in-plant observations, measurements, and evaluations.
Principle 7: Documentation
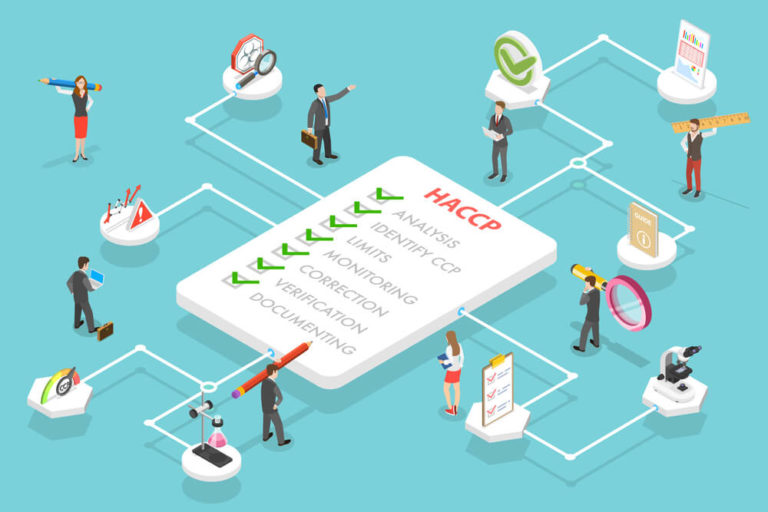

The final principle is to record everything of the HACCP food safety management system and to keep records of all procedures. Here is what the documentation must include:
- Document the HACCP plan for your food business. Record all the ingredients, utensils and cooking and freezing appliances.
- Details of the team who will carry out the HACCP plan
- Description of all the foods, their distribution, their use and consumers
- A detailed summary of the hazard analysis, along with the reasoning for evaluating hazards and control measures.
- Verified flow diagram
- Steps in the process that are CCP
- The hazard of concern.
- Critical limits
- Monitoring
- Corrective actions
- Verification procedures and the timing of the procedure
- Record-keeping procedures
- Supporting details like validation records.
- Records that are made during the operation of the HACCP plan.
Serve The Healthiest Food
The world is filled with food critics and food bloggers. There can be a great issue for a minor mistake. General people are more health-conscious than ever and are very critical about what goes on their plate. As a food business owner and chef, you must be very serious about food safety management. Complete expertise in HACCP is a must in this case.
In order to know more about the 7 principles of HACCP and to become a food safety expert, join our HACCP Complete Bundle course. Learn the principles in details and how to make a high-quality HACCP plan for your own business with us.
- Available Courses
- Animal care10
- Design36
- Training10
- Accounting & Finance Primary51
- Teaching & Academics Primary37
- Teaching23
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed181
- Law10
- IT & Software238
- Job Ready Programme52
- Charity & Non-Profit Courses28
- HR & Leadership4
- Administration & Office Skills6
- Mandatory Training36
- Regulated Courses4
- AI & Data Literacy29
- Health and Social Care291
- Personal Development1666
- Food Hygiene119
- Safeguarding81
- Employability288
- First Aid73
- Business Skills301
- Management426
- Child Psychology41
- Health and Safety538
- Hospitality28
- Electronics30
- Construction63
- Career Bundles201
- Marketing39
- Healthcare174
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development





