
In this article ...
What is a confined space?
Limited openings for entry and exit
Adverse natural ventilation
Unfavourable for continuous worker occupancy
The law regarding work safety in confined spaces
Under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999, you have to carry out adequate confined space risk assessment. In general, the assessment includes:
- the task,
- the working environment,
- working materials and tools,
- the suitability of those carrying out the task,
- arrangements for emergency rescue.
You will be required to appoint people to manage the risks and train the employees adequately. If you identify risks of serious injury in a confined space, the Confined Spaces Regulations 1997 will apply. These regulations points to the key duties listed below:
- Working from outside and avoid entry to the confined space;
- Following a safe system of work if entry to the space is unavoidable;
- Making appropriate emergency arrangements before the work starts.
The potential risks of working in a confined space
Hazardous atmosphere
The atmosphere of a confined space could be extremely hazardous due to the lack of natural air circulation. Consequently, a confined space can have 1) oxygen-deficient atmospheres, 2) flammable atmosphere, 3) toxic atmosphere.
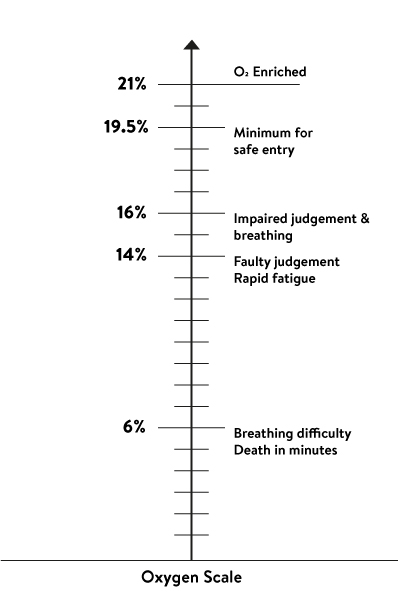
Oxygen-deficient atmosphere
If the level of oxygen is less than 19.5% in a confined space, the atmosphere is oxygen-deficient. For working in this type of atmosphere, you need an approved self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA).
The oxygen level can drop because of welding, cutting, soldering, chemical reactions (rusting) or bacterial action (fermentation). Another gas like nitrogen or carbon dioxide can displace oxygen. So, the oxygen level will decrease. Total replacement of oxygen will result in unconsciousness, and death subsequently.
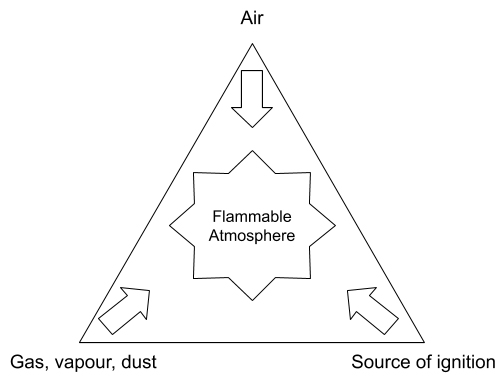
Flammable atmosphere
An atmosphere could be flammable if (a) there is the oxygen in the air, and (b) a flammable gas, vapour, or dust in a specific proportion. A source of ignition in the form of a spark or electrical tool can cause an explosion in an ignitable atmosphere.
An atmosphere which is rich with oxygen above 21% will make flammable materials like fabric and hair burn fiercely. Thus, you should never use pure oxygen for ventilation in a confined space. Use normal air to ventilate.
Toxic atmosphere
General hazards
Extreme temperature
People would find it difficult to work in extreme hot or cold temperatures. It is necessary to allow a confined space to cool down before entering the space if it has been steamed.
Engulfment hazard
Noise
Falling object
Slick or wet surface
Safety tips for working in a confined space
A video about the risks and safety rules for confined spaces in ports (Source: Ports Skills and Safety)
Carry out a detailed risk assessment for confined space
Try to avoid entry to the confined space altogether if there is an alternative
It sounds insensible but it is an option. With the advancement of technology, you can work remotely using handy tools. Don’t volunteer to enter confined spaces. You might get into trouble and endanger the lives of your colleagues. Ask yourself whether the task is mandatory or not. Can you modify the space itself so that the entry won’t be required? You can get the work done from outside. For example, you can:
- Clean blockages in silos using remotely operated rotating flail devices, vibrators or air purgers.
- Inspect, collect samples or perform cleaning operations from outside the space using suitable equipment.
- Do an internal inspection of vessels with remote cameras
Get a permit for entering the confined space
Everyone who enters a confined space must sign a permit-to-work. The document requires the consents of all the parties including the issuing and performing authorities. The permit-to-work ensures that all the elements of workplace safety are in place before people can enter or work in the confined space. The permit-to-work is also a means of communication between site management, supervisors and workers involved in the hazardous tasks. The key features of the permit are:
- Clear identification of the authorised people responsible for specifying particular jobs and necessary precautions (e.g. isolation, air testing, emergency arrangements etc.)
- The contractors involved in the tasks are included
- Confined space training and instructions in the issue of permits
- Risk assessment and monitoring to ensure the application of the system
Monitor the atmosphere of the confined space consistently
Keep all the necessary tools in place
Plan escape routes in advance
Ensure assisted ventilation
Have an emergency team standby
Read more on our blog
- The Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS)
- Sports First Aid | Everything You Need To Know
- Lots of Likes on Instagram: How You Can Quickly Increase Popularity
- Why You Should Use Photo Background Removers For Mobile Devices
- Maximizing ROI: 11 Strategies For Efficient Advertising Spend
- How to Keep Your Data Safe While Applying for Jobs: 6 Tips
- Take Mac Classes to Transform Your Design Profession
- Exploring the landscape of e-commerce hosting
- Personal Branding For Executives: 7 Tips For Maximum Impact
- Transformative Technologies in Senior Living Homes: A Glimpse into 2024
- Available Courses
- Career Bundles73
- Animal care5
- Law8
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed111
- Teaching13
- Teaching & Academics Primary27
- Accounting & Finance Primary30
- Training3
- Design9
- IT & Software44
- Healthcare126
- Marketing31
- Health and Safety402
- Construction48
- Electronics25
- Hospitality22
- Health and Social Care219
- Child Psychology37
- Management377
- Business Skills268
- First Aid70
- Employability264
- Safeguarding75
- Food Hygiene103
- Personal Development1277
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development








