

Feeling challenged by the problems in your business? Looking for creative and strategic ways of solving problems? Your journey can start with critical thinking and problem-solving training. In a business environment, you are always searching for opportunities. Problems are opportunities in disguise. To become a problem-solver, you are on a mission to learn the art of thinking critically and creatively.
You need to find innovative solutions to your problems which will derive from teamwork and collaboration. Let’s explore the key concepts of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
In this article ....
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking and problem-solving: Why should you have the skills?
- Improves flexibility and learning skills. With the evolutionary changes in technology, you have to learn and adapt faster to new environments and procedures. Critical thinking helps us to be more flexible to changes.
- Students can reflect on their learning experiences critically and make effective decisions.
- With critical thinking, you can take apart facts from opinionated facts. You start considering all possible options for reaching a prospective solution.
- In the field of education, students tend to become more interactive if the teacher encourages them to think critically. With critical thinking, students can align their subjects with their own lives. In the process, learners become active participants in the whole learning process.
- While solving problems, students also learn other important skills such as creativity, collaboration, and cooperation.
- Encourages the practice of reasoning that helps us to overcome biases and prejudices.
- Critical thinking skills enhance performance as you are self-directed in your learning and decision-making.
How relevant is critical thinking to your job?
Manager
Managers are role models for their teams. As a manager, your ability to analyse problems critically influence your team members in the long run.
Human Resources Specialist
Lawyer
Business Analyst
Accountant
Marketing Associate
Marketing associates gather and analyse a wide range of information regarding the target audience for their organisations. The ability to think critically can influence them to work out different solutions for successful marketing campaigns.
Sales Agent and Customer Service Representative
Creative ways of solving problems: the problem-solving method

-
A balance of divergent and convergent thinking
Divergent and convergent thinking is one of the key factors creative problem-solving. Both processes have their distinct features. You need to make sure that you are using the processes effectively.
-
Rephrase your problems and challenge statements as questions
Ask open-ended questions rather than closed questions that provoke short answers.
-
Limit your judgemental instincts
According to Alex Osborn, challenging solutions at the earlier stage impedes the idea generation process. Analyse the solutions at a later stage when all the solutions are on the table after primary brainstorming.
-
Positive language focus
Language has a big impact on our thinking process. We need to encourage the use of “Yes, and .” rather than “No, but …”. Words like ‘but’ take conversations to an end and bring negative energy in the initial brainstorming process.
Another popular model of creative problem-solving (CPS) is CPS Learner’s Model. The model can be useful for generating innovative solutions.
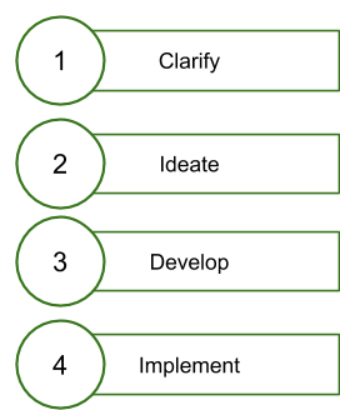
1. Clarify
Start identifying your goals, desires or challenges. Don’t make wild assumptions about your problem. Define your objectives clearly for clarity. Gather data about the problem. You can interview people, conduct surveys and collect statistics. Try to understand everyone’s opinions and feelings. Formulate open-ended questions based on your awareness of the problems. Visualise the challenges and opportunities regarding the problem.
2. Ideate
It’s time for brainstorming, brain writing, mind mapping or other forms of idea generating techniques. This is where creativity matters. When you get tired of the continuous process, take a break and return with fresh ideas. Problem Solving Skills discusses elaborately on the preparation for brainstorming.
3. Develop
Now you are moving to the convergent stage of creative problem-solving. Your focus shifts to the evaluation of all the ideas generated before. Analyse the potential solutions, and think of the rationale behind the implementation of the solution.
4. Implement
You have to plan the course of action for the implementation stage. Identify your resources, communicate with the stakeholders and explain everything to the implementer.
Some ways of generating ideas creatively
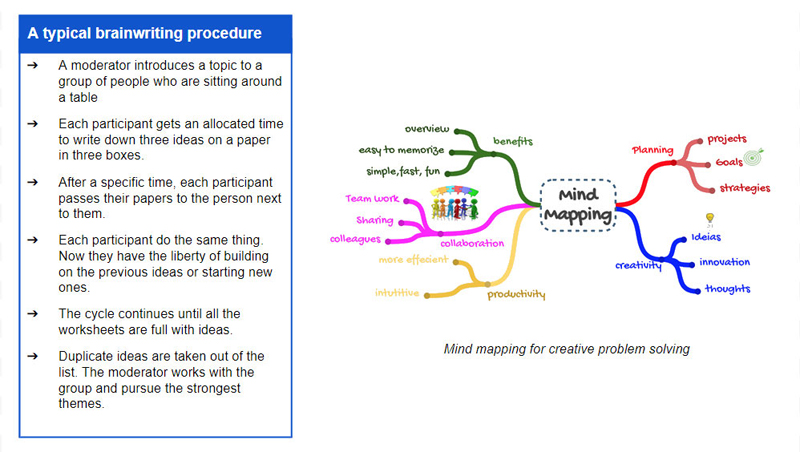
Brainwriting: Brainwriting is a complementary technique to brainstorming. It can be considered a graphic version of brainstorming. Horst Geschka and his colleagues gave the idea as part of their research on the innovation management method.
Mind mapping: Mind maps are a visual representation of ideas on a piece of paper. You put the central idea in the middle and the associated ideas surrounding the central concept. Afterwards, you connect the ideas.
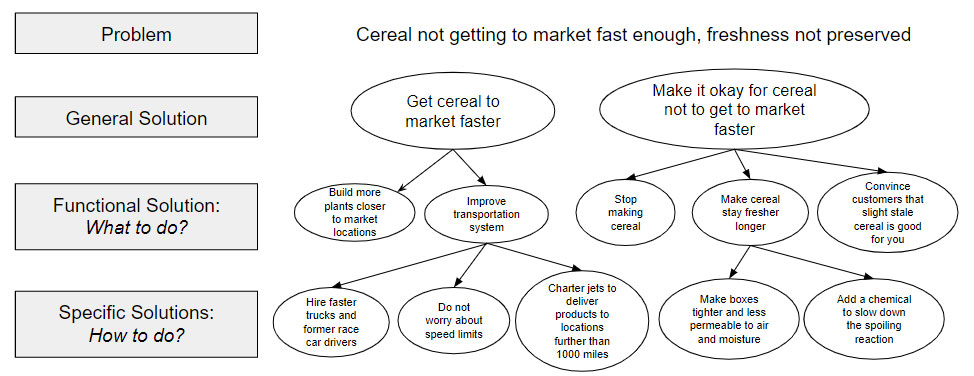
Duncker diagram: A comparative flowchart of the present state and desired state side by side with general solutions, functional solutions and specific solutions in three different levels.
How can a course on critical thinking help you to solve problems?
From our course on critical thinking and problem-solving, you will familiarise with the following concepts:
- Understanding and defining problems for creative problem-solving
- Using your existing resources more productively to generate ideas
- Thinking outside the box overcoming personal limitations
- Gaining knowledge on the different phases of the creative problem-solving process
- Utilising popular models in your way to gather information about problems and solutions
- Working with team members and implementing established brainstorming techniques for practical solutions to problems.
The modules of the course cover topics like problem-solving methods, information-gathering techniques, defining problems for clarity, getting ready for effective brainstorming, generating solutions maintaining a specific sequence, solutions analysis and planning the implementation phase.
Learn More
- Available Courses
- Animal care10
- Design36
- Training10
- Accounting & Finance Primary51
- Teaching & Academics Primary37
- Teaching23
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed181
- Law10
- IT & Software236
- Job Ready Programme52
- Charity & Non-Profit Courses28
- HR & Leadership4
- Administration & Office Skills6
- Mandatory Training36
- Regulated Courses4
- AI & Data Literacy29
- Health and Social Care291
- Personal Development1663
- Food Hygiene119
- Safeguarding81
- Employability288
- First Aid73
- Business Skills300
- Management426
- Child Psychology41
- Health and Safety538
- Hospitality28
- Electronics30
- Construction63
- Career Bundles201
- Marketing39
- Healthcare174
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development





