
The ABC chart analyses behaviour by identifying antecedents, behaviours, and consequences.
The ABC chart stands for
- A: Antecedent – the events or stimuli that occur immediately before the behaviour
- B: Behaviour – the specific behaviour being observed or measured
- C: Consequence – the events or stimuli that occur immediately after the behaviour
Track antecedents, behaviours, and consequences to identify behaviour patterns and facilitate modification.
ABC charts identify triggers and develop intervention strategies for challenging behaviour in therapy and classroom settings.
Table of Contents
What is the ABC model of challenging behaviour?
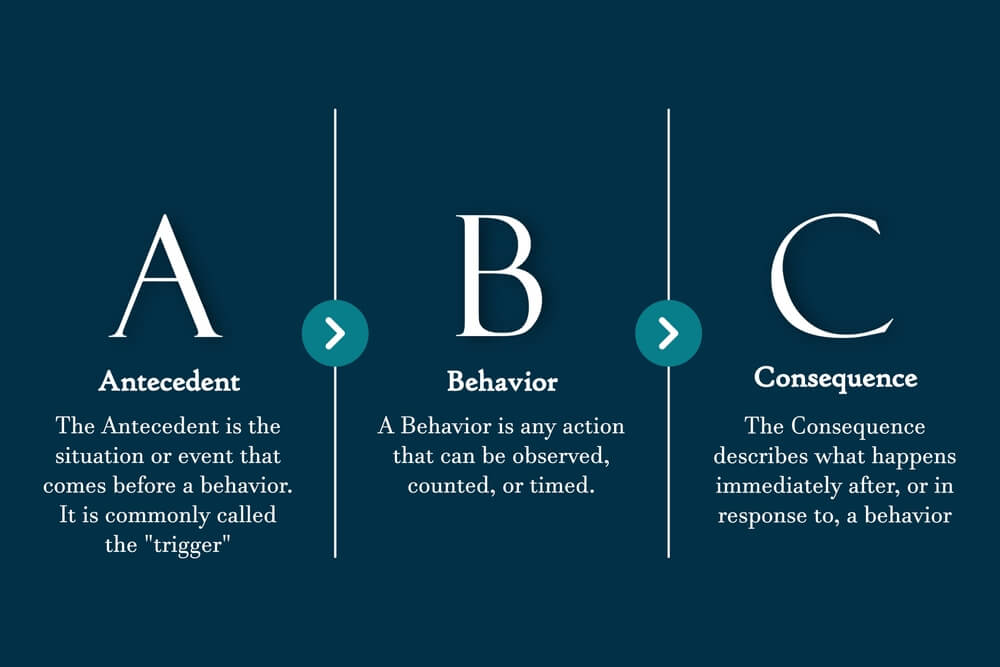
The ABC model manages challenging behaviour by examining antecedents (A), behaviour (B), and consequences (C).
The ABC model proposes:
- Antecedents (A) are the events or triggers that occur before the challenging behaviour. Antecedents include environmental, social, or other factors that contribute to behaviour.
- Behaviour (B) is the identified specific challenging action or behaviour. Physical, verbal, or a combination of the two types of behaviour are possible.
- Consequences (C) – These are the events that occur immediately following the behaviour. For example, Consequences include reactions, outcomes, or rewards/punishments that follow the behaviour.
The ABC model helps determine the root causes of challenging behaviour and change antecedents or consequences to reduce or eliminate it.
Are you a behaviour support worker or childminder who wants to improve your ability to manage challenging behaviour?
Gain a deep understanding of challenging behaviour triggers and tools to manage them effectively through our program’s modules.
Our evidence-based approach and techniques help create a safer and more supportive environment for those in your care.
Enrol in our behaviour support worker training program to make a positive impact on individuals’ lives.
Don’t wait – sign up now to improve your skills and start making a difference today.
What are the 4 functions of behaviour ABC?

Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA) identifies four primary functions of behaviour using the ABC model.
- Attention
The behaviour is used to attract or interact with others. A child, for example, may engage in challenging behaviour, such as hitting or yelling, to gain the attention of a parent or caregiver.
- Escape
The behaviour is used to avoid or escape from a difficult or unpleasant situation or task. To avoid a difficult academic task, a student may engage in challenging behaviour, such as leaving the classroom or refusing to work.
- Access to tangibles
This behaviour is used to obtain desired items or activities. For example, a child may engage in challenging behaviour, such as throwing a tantrum, to obtain a desired toy or snack.
- Sensory
The behaviour is used to stimulate the senses or to relieve sensory discomfort. Challenging behaviour, like head-banging, can be a child’s way of relieving pain or stimulating the senses.
Understanding how behaviour works is essential for developing effective intervention strategies. Addressing underlying causes, like teaching alternative behaviours or changing the environment, can reduce or eliminate challenging behaviour.
→ Accredited by CPD
→ Self paced learning
→ Instant FREE certificate upon completion
→ Unlimited FREE retake
How to create an ABC Chart for a child with challenging behaviour
Follow these steps to make an ABC chart for a child with challenging behaviour:
Define the behaviour as follows
Determine which behaviour you want to track and measure. Make your definition of the behaviour clear and specific so that it is consistent and measurable.
Determine the causes and consequences
Observe the child’s behaviour, and record antecedents (before) and consequences (after). Gather data from observation, interviews, and documentation review.
Make the ABC chart as follows
Make a table with three columns labelled “Antecedent,” “Behaviour,” and “Consequence.” In the appropriate columns, record each instance of the behaviour as well as the antecedents and consequences.
Analyse the data
Use the ABC chart to identify behaviour patterns and triggers after gathering information. Examine the environment for common antecedents or consequences that contribute to the behaviour.
Create intervention strategies based on data analysis
Create intervention strategies to change antecedents or consequences. Modify the environment to reduce or eliminate the trigger if the behaviour is environment-specific.
Monitor Progress
Continue to use the ABC chart to track progress and assess the effectiveness of your intervention strategies. Make any necessary changes to attain the desired outcomes.
Involve caregivers, teachers, and professionals who work with the child in creating and using the ABC chart for a comprehensive behaviour management approach.
Download Free Template : ABC Chart for Challenging Behaviour
Modify this ABC Chart : Canva Link
Examples of ABC Charts for Challenging Behaviour
Here are some examples of ABC charts for challenging behaviour:
Example 1: Aggressive behaviour in a child with autism
Antecedent | Behaviour | Consequence |
Teacher gives instruction | The child hits or kicks the teacher | The teacher gives attention, child removed from the activity |
Example 2: Tantrums in a child with ADHD
Antecedent | Behaviour | Consequence |
The parent asks the child to stop playing video games | The child screams and throws objects | The parent gives in, the child continues playing video games |
Example 3: Noncompliance in a student with a learning disability
Antecedent | Behaviour | Consequence |
The teacher gives task instruction | The student refuses to work and throws materials | The teacher sends the student to the principal’s office |
In each of these examples, the ABC chart is used to track and analyse the antecedents, behaviour, and consequences of the challenging behaviour. By identifying patterns and potential triggers of the behaviour, caregivers and professionals can develop effective intervention strategies to reduce or eliminate the occurrence of challenging behaviour.
Understanding the Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence Model

The ABC model is a framework for analysing behaviour and its environment. Every behaviour is influenced by antecedents (before) and consequences (after). The model is predicated on this notion.
The ABC model is made up of three parts:
- The event or situation that occurs immediately before the behaviour is referred to as the antecedent. The behaviour can be triggered by a specific stimulus, instruction, or situation.
- The observable action or response that occurs in response to the antecedent is referred to as behaviour. It can be either physical or verbal.
- The event or situation that occurs immediately following the behaviour is referred to as the consequence. It can be a reinforcement (something that makes the behaviour more likely to occur again) or a punishment (something that decreases the likelihood of the behaviour occurring again).
Behaviour analysts can identify the factors that influence a behaviour and develop interventions to modify those factors by analysing its antecedents and consequences.
Assume a child has a temper tantrum every time he is asked to do his homework (behaviour). The antecedent could be the assignment of homework, and the result could be that the child is permitted to avoid the task. The behaviour analyst can reduce the likelihood of a tantrum occurring by changing the antecedent or consequence, such as providing more motivating instruction or withholding a preferred activity until the homework is completed.
The ABC model is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between behaviour and environment, and It can be used for a wide range of behaviours and events.
→ Accredited by CPD
→ Self paced learning
→ Instant FREE certificate upon completion
→ Unlimited FREE retake
Benefits of Implementing an ABC Chart in Behaviour Management
There are several benefits to implementing an ABC chart in behaviour management, including
Understanding the function of the behaviour
By using an ABC chart to track the antecedents and consequences of a behaviour, you can better understand why the behaviour is occurring. This can help you develop more effective interventions that target the underlying cause of the behaviour.
Individualising interventions
By analysing the data on the ABC chart, you can develop interventions that are tailored to the specific needs of the individual. This can lead to more effective behaviour management and better outcomes for the individual.
Identifying triggers
By tracking the antecedents of behaviour, you can identify specific triggers that may be contributing to the behaviour. This can help you modify the environment or the individual’s routine to reduce the occurrence of the behaviour.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Interventions
Monitoring the effects of a behaviour allows you to assess the success of interventions and make changes as needed. This can help you determine whether an intervention is working or whether you need to try a different approach.
Improving communication
An ABC chart can also be useful for improving communication between parents, teachers, and other professionals who work with the individual. By sharing the data on the ABC chart, everyone can be on the same page and work together to develop effective interventions.
Overall, an ABC chart can help manage and improve challenging behaviours in individuals. Tracking ABC can develop individualised interventions. Interventions target underlying cause of behaviour. ABC chart leads to better outcomes for individuals.
When to use an ABC chart for challenging behaviour

An ABC chart is a useful tool for gathering information about challenging behaviour and identifying patterns and triggers. Here are some situations in which you may want to use an ABC chart for challenging behaviour:
When behaviour is interfering with learning or daily activities
Suppose a child’s behaviour is interfering with their ability to learn or participate in daily activities. In that case, use an ABC chart to gather information about the behaviour and develop strategies to address it.
When behaviour is causing harm or safety concerns
Suppose a child’s behaviour is putting themselves or others in danger. In that case, it is important to gather information about the behaviour to identify patterns and develop effective interventions to prevent the behaviour from escalating.
When behaviour is impacting social relationships
Suppose a child’s behaviour is impacting their social relationships or ability to interact with others. In that case, an ABC chart can be useful in identifying triggers and developing strategies to promote positive social interactions.
When previous interventions have been ineffective
If previous interventions for challenging behaviour have been ineffective, an ABC chart can provide valuable information to help professionals identify underlying causes and develop more effective interventions.
When a functional behaviour assessment (FBA) is warranted
An ABC chart is often used as part of a comprehensive FBA, which involves gathering information about the antecedents, behaviour, and consequences of the behaviour to develop a functional analysis and develop effective interventions.
Overall, an ABC chart useful for challenging behaviour in various situations. Chart gathers information and identifies patterns. Professionals can develop effective interventions. Interventions support individual and promote positive behaviour.
Antecedents and Consequences in an ABC Chart
An ABC chart can help identify triggers for challenging behaviour, such as praise, changes in activity, sensory stimulation, lack of interest, hunger, and disturbances in routines.
Consequences that follow behaviour can either reinforce or discourage future occurrences. Examples include praise, reassurance, breaks, confrontation, and punishment.
A child may exhibit behavioural responses to antecedents such as praise, requesting changes, receiving “no,” sensory stimulation, playing without instruction, observations, lack of interest, hunger, time of day, energy level, medication, changes in routine, and presence of certain people.
Consequences such as praise, reassurance, breaks, confrontation, and punishment can influence the likelihood of future occurrences of the behaviour.
The Role of Consequences in Managing Challenging Behaviours

ABC chart identifies Antecedent, Behavior, and Consequence of troublesome behaviour.
Consequences can encourage or diminish behaviour recurrence.
When an action occurs, it is critical to identify the resulting consequence. Consequences can be good or negative, raising or decreasing the likelihood that the behaviour will occur again. Positive consequences, such as praise, awards, or attention, are reinforcement. Punishment refers to negative repercussions like reprimands or time-outs.
It is critical to recognise that consequences are not always intended or anticipated. Identifying all consequences, intentional or unintentional, is crucial.
Therefore, abc chart useful in comprehending function of consequences in challenging behaviour management.
The ABC chart is a useful tool for recognising and comprehending the function of consequences in challenging behaviour management. Recording ABC can identify patterns and determine reinforcing or decreasing likelihood of behaviour.
In summary, consequences either reinforce or reduce likelihood of behaviour recurrence. ABC chart useful in recognizing and comprehending consequences function in managing problematic behaviours.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the abc chart identifies antecedents, behaviours, and consequences of difficult behaviours. Helps caregivers understand behaviour and develop management methods. Useful in homes, schools, hospitals, and with people of all ages. Not a stand-alone intervention but a tool for guiding behaviour support. Therefore, work with trained professionals to develop appropriate interventions based on the chart. Overall, encourages positive behaviour change and improves the quality of life.
→ Accredited by CPD
→ Self paced learning
→ Instant FREE certificate upon completion
→ Unlimited FREE retake
FAQ(s) on ABC Chart for Challenging Behaviour
An ABC chart is a tool used to understand and record challenging behaviours. It stands for Antecedent, Behaviour, and Consequence. It helps spot patterns in why a behaviour might be happening.
ABC stands for:
- Antecedent: What happened just before the behaviour?
- Behaviour: What was the actual behaviour seen?
- Consequence: What happened right after the behaviour?
By keeping track of when and why challenging behaviours happen, you can work out patterns. Spotting these patterns can help come up with ways to manage or change the behaviours.
You can find ABC chart templates here.
Chart-for-Challenging-Behaviour-Download-Free-Template
You can modify sections as per your requirement for noting down the Antecedent, Behaviour, and Consequence.
All electrical appliances that have a plug and are intended for connection to the mains electricity supply should be considered for PAT testing. This includes computers, printers, refrigerators, kettles, and even extension leads.
- Appliances connected to the mains electricity supply should be considered.
- This encompasses a wide range of items, from computers to kettles.
- Even extension leads are included in the list.
While the ABC chart is often used for challenging behaviours, it can be used to track any behaviour you want to understand better.
When you see a behaviour you want to track:
- Note down what happened just before it in the 'Antecedent' section.
- Describe the actual behaviour in the 'Behaviour' section.
- Write what happened straight after in the 'Consequence' section.
You can use the ABC chart for anyone, whether they're adults or kids. It’s all about understanding behaviour better.
Update the chart every time you notice the behaviour. The more info you have, the better you can spot patterns.
That's okay. Just write down what you do know. Over time, you might start to see the missing bits of the puzzle.
Absolutely! While it’s often used for challenging behaviours, it's great for positive ones too. It helps understand what encourages good behaviour.
- Available Courses
- Career Bundles73
- Animal care5
- Law8
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed111
- Teaching13
- Teaching & Academics Primary27
- Accounting & Finance Primary30
- Training3
- Design9
- IT & Software44
- Healthcare126
- Marketing31
- Health and Safety402
- Construction48
- Electronics25
- Hospitality22
- Health and Social Care219
- Child Psychology37
- Management377
- Business Skills268
- First Aid70
- Employability264
- Safeguarding75
- Food Hygiene103
- Personal Development1277
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development







